With the recent breakthrough discoveries of DAAs in treating HCV, it is widely believed that HCV is now curable in the majority of patients. The focus of research is now shifting to HBV, hoping to copy the success story of HCV.
Hendrik W. Reesink MD, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, reported the outcome of the phase II clinic trial of REP2139-Ca, a nucleic acid polymer (NAP), a promising new treatment option that is being tested to treat HBV infection by inhibiting HBsAg release with the title “Serum HBV-RNA levels decline significantly in chronic hepatitis B patients dosed with REP2139-Ca.”
The trial aim was to test the effect of REP2139-CA on HBV-DNA and HBsAg levels in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients. In total, 12 patients with HBeAg-positive CHB were treated with nucleic acid based amphipathic polymer REP2139-Ca for 20-38 weeks. If the patients responded to REP2139 with clearance of serum HBsAg, the patients would be subsequently treated with an add-on immunomodulatory agent - pegylated interferon alpha-2a and/or thymosin alpha-1. If the patients didn’t respond to the treatment, entecavir treatment followed.
HBsAg, HBV-DNA, and HBV-RNA levels were determined at baseline, after 20-24 weeks of REP2139-Ca monotherapy, and either during a treatment-free follow-up (for responders) or during entecavir treatment.
The results demonstrated that HBV-RNA levels were detectable in all 12 HBeAg-positive patients before treatment with a mean of 6.70 (SD 0.83) logC/mL. After 20-24 weeks of REP2139-Ca treatment, mean HBV-RNA, HBV-DNA, and HBsAg levels had declined significantly compared to baseline (P<0.001).
At week 20-24, HBV-RNA was undetectable in 8/12 patients. In 7 of these 8 patients, HBV-RNA remained undetectable during the treatment-free follow-up period (mean 21.9 weeks, range 7-27). HBsAg seroconversion was achieved in 4/8 patients during follow-up with anti-HBs ranging from 200-766 U/L.
In conclusion, in patients treated with REP2139-Ca, serum HBV-RNA levels decreased significantly compared to baseline. REP2139-Ca may be a promising new treatment option for CHB patients, according to Dr. Reesink.
The trial was funded by Replicor Inc.
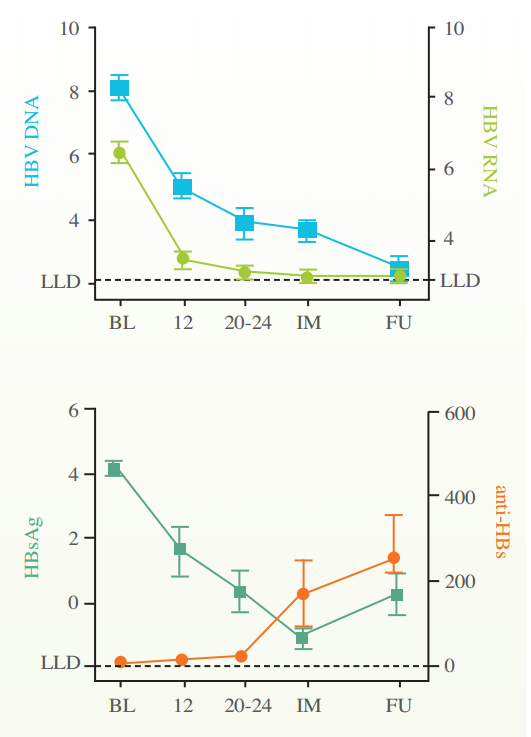
Serum HBV-RNA in REP2139-Ca Responders
发表评论
全部评论